In the world of Forex trading, understanding the various types of orders in Forex is essential for managing trades effectively. These orders allow traders to specify how they want their trades to be executed, giving them control over factors such as entry and exit points, risk management, and overall strategy. The different types of orders in Forex provide flexibility and precision, helping traders navigate the fast-paced and volatile nature of the Forex market.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, knowing how to use these orders is crucial for maximizing profits and minimizing risks. Some of the most common orders include market orders, limit orders, stop-loss orders, and trailing stops. Each of these orders serves a unique purpose, and by learning how to apply them effectively, traders can enhance their decision-making process and protect their investments in the Forex market.
Table of Contents
How Does a Market Order Work in Forex Trading?
A market order is one of the most straightforward order types in Forex trading. When you place a market order, you are instructing your broker to execute a trade at the current market price. This type of order ensures that your trade is filled immediately, making it ideal for traders who want to enter or exit a position quickly without waiting for specific price levels.
1. Instant Execution
A market order guarantees that your trade will be executed at the best available price in the market. This makes it the go-to option for traders who prioritize speed over precision.
- Advantages: Market orders are ideal for volatile markets where prices move quickly, as they ensure fast execution.
- Disadvantages: You may experience slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price), especially during high volatility periods.
2. When to Use Market Orders
- Entering/Exiting Trades Quickly: Use market orders when you need to enter or exit a position immediately, without waiting for a specific price level.
- High Liquidity Situations: Market orders are effective in highly liquid markets, such as major currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD, where slippage is less likely.
What Is a Limit Order and How Can You Use It in Forex?
A limit order allows you to specify the price at which you want your trade to be executed. Unlike market orders, limit orders are not filled immediately but instead are placed at a price better than the current market price. This gives traders greater control over their entry and exit points, making them a useful tool for precision trading.
1. Types of Limit Orders
- Buy Limit Order: A buy limit order is placed below the current market price, and the trade will only be executed when the market price reaches the set level. This is used when traders expect the price to drop before reversing upward.
- Sell Limit Order: A sell limit order is placed above the current market price, and the trade will only be executed when the price rises to that level. It’s used when traders expect the price to rise before falling.
2. When to Use Limit Orders
- Control Over Entry/Exit Points: Limit orders are ideal when you want to set precise entry or exit points and don’t want to trade at the current market price.
- Avoiding Slippage: By setting a limit price, you avoid the risk of slippage that can occur with market types of orders, ensuring that your trade is only executed at your specified price.
How Do Stop Orders Work and When Should You Use Them in Forex?
A stop order is designed to trigger a trade when the market reaches a specific price level. Stop orders are commonly used for risk management, allowing traders to set price levels where they want to either enter or exit a position. There are two main types of stop orders: buy stop and sell stop.

1. Types of Stop Orders
- Buy Stop Order: A buy stop order is placed above the current market price, and it triggers a buy trade when the market reaches that level. This is often used in breakout trading strategies, where traders expect the price to continue rising once a certain level is breached.
- Sell Stop Order: A sell stop order is placed below the current market price, and it triggers a sell trade when the price falls to that level. It’s commonly used as a stop-loss order to limit potential losses.
2. When to Use Stop Orders
- Breakout Trading: Use a buy stop or sell stop order when trading breakouts, where you anticipate the price to move significantly once it breaks a key level of resistance or support.
- Risk Management: Stop orders, especially stop-loss orders, are essential tools for managing risk. They ensure that your losses are limited if the market moves against your position, automatically exiting the trade when a specified price is reached.
What Is the Difference Between Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders in Forex?
Both stop-loss and take-profit orders are critical tools for managing risk and securing profits in Forex trading. They allow traders to automate their trades by specifying exit points, reducing the need for constant monitoring of the markets.
1. Stop-Loss Order
A stop-loss order is designed to limit losses by automatically closing a trade when the market moves against your position to a specified price. For example, if you open a long position on EUR/USD at 1.2000 and set a stop-loss at 1.1950, your trade will automatically close if the price drops to 1.1950, limiting your losses.
- Risk Management Tool: Stop-loss orders are essential for protecting capital and avoiding large, unexpected losses in volatile markets.
- Common Usage: Traders use stop-loss orders in conjunction with market or limit orders to ensure that their trades are exited before significant losses occur.
2. Take-Profit Order
A take-profit order is the opposite of a stop-loss. It automatically closes a trade when the price reaches a pre-set level of profit. If you place a take-profit at 1.2050 after entering a long position at 1.2000, your trade will close once the price reaches 1.2050, locking in your profits.
- Profit Automation: Take-profit orders ensure that you lock in profits without having to manually close the trade when the market reaches your target.
- When to Use It: These orders are ideal for traders who want to automate profit-taking and avoid emotional decision-making during price fluctuations.
Key Differences:
- Purpose: Stop-loss orders minimize risk by limiting losses, while take-profit orders maximize gains by securing profits.
- Placement: Stop-loss orders are placed below the entry price for buy positions and above for sell positions, while take-profit orders are placed in the opposite direction.
How Can a Trailing Stop Order Help You Lock in Profits?
A trailing stop order is a dynamic version of the traditional stop-loss order that adjusts as the market price moves in your favor. This order allows traders to lock in profits while also protecting their trades from potential reversals, making it a flexible risk management tool.
1. How a Trailing Stop Works
Instead of being fixed, a trailing stop moves with the market price. For example, if you set a trailing stop 50 pips below your entry price in a long position, and the price rises, the stop-loss will automatically trail behind the market by 50 pips. If the price moves in your favor, the trailing stop moves up; if the price reverses, the trade will close when the stop is hit.
- Automatic Adjustment: The trailing stop “locks in” profits as the price moves in your favor, ensuring that you don’t lose out on gains if the market reverses.
- Protecting Gains: As the market moves, the trailing stop follows, ensuring that your gains are protected without limiting your upside potential.
2. When to Use a Trailing Stop
- Trending Markets: Trailing stops are particularly useful in trending markets where the price is expected to continue moving in the same direction for a significant period.
- Automating Risk Management: This type of stop order is helpful for traders who want to maximize profits without manually adjusting their stop-losses as the market moves.
Advantages of Trailing Stops:
- Lock in Profits Automatically: You don’t have to manually monitor your trade to secure profits.
- Reduce Emotional Trading: Trailing stops remove the need for emotional decision-making as the market fluctuates, helping you stick to your trading plan.
What Are Pending Orders in Forex and How Do They Work?
Pending orders in Forex are instructions to execute a trade at a later time when the market reaches a specific price level. Unlike market orders, which are executed immediately at the current price, pending orders allow traders to plan their trades in advance and automate execution.
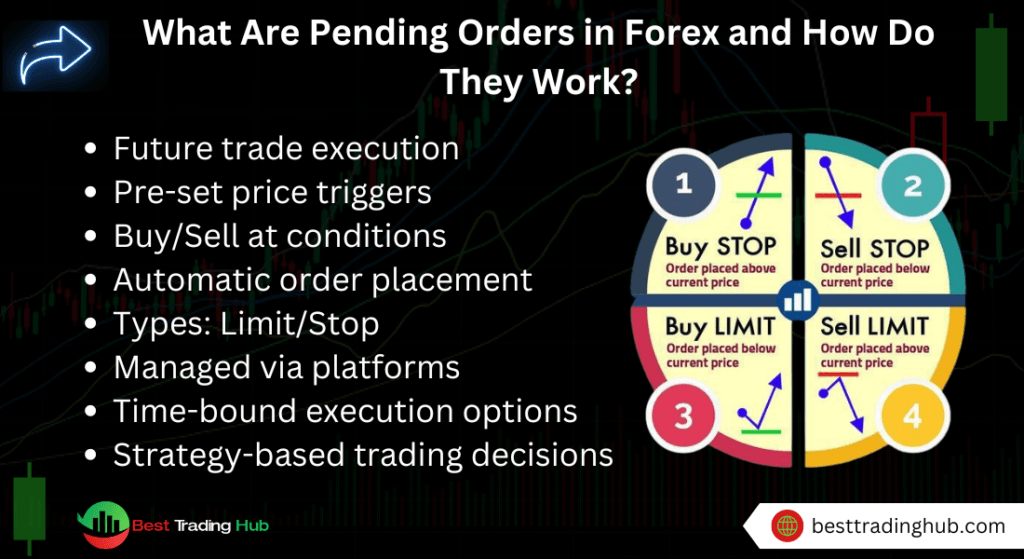
1. Types of Pending Orders
There are two main types of pending orders: limit orders and stop orders. Each serves a specific purpose depending on whether the trader expects the price to reverse or break out.
- Buy Limit and Sell Limit Orders: Limit orders allow you to buy below the current price (buy limit) or sell above the current price (sell limit). They are typically used in range-bound markets where traders anticipate a reversal.
- Buy Stop and Sell Stop Orders: Stop orders allow you to buy above the current price (buy stop) or sell below the current price (sell stop), often used for breakout strategies where the trader expects the price to continue in the current direction once a key level is breached.
2. When to Use Pending Orders
- Automation and Flexibility: Pending orders allow traders to enter the market at specific levels without needing to monitor the markets constantly. This is especially useful for traders who anticipate a price movement but don’t want to execute a market order right away.
- Breakout Strategies: Stop orders are ideal for traders using breakout strategies, as they automatically trigger a trade once the price moves past a certain level, allowing the trader to capitalize on the momentum.
Advantages of Pending Orders:
- Precision: Pending orders help traders execute trades at precise price points, reducing the risk of entering the market at unfavorable prices.
- Reduced Monitoring: By using pending types of orders, traders can automate their strategies and focus on other aspects of their trading plan.
How to Use a Good ‘Til Canceled (GTC) Order in Forex Trading?
A Good ‘Til Canceled (GTC) order is a type of pending order that remains active until the trader either cancels it or the trade is executed. Unlike other order types with time limits, such as day orders, GTC orders provide flexibility for traders who want to hold their positions open for an extended period, waiting for a specific price level to be reached.
1. How GTC Orders Work
With a GTC order, you can place a buy or sell order at a specific price and leave it active until it’s either filled or manually canceled. This is useful for traders who don’t want to constantly monitor their positions but still wish to enter the market when a particular price is reached.
- Flexibility: GTC orders give traders the convenience of placing long-term orders that don’t expire at the end of the trading day.
- Risk of Overlooking: Since GTC orders remain active indefinitely, traders should monitor them to avoid potential unintended executions during unforeseen market conditions.
2. When to Use GTC Orders
- Long-Term Trading: GTC types of orders are ideal for traders with long-term strategies who want to target specific price levels without worrying about daily expiration.
- Precision Entry: If you’re waiting for a very specific price to be hit—whether buying low or selling high—a GTC order allows you to automatically enter or exit when that price is reached.
Advantages of GTC Orders:
- No Time Limit: Unlike day types of orders, GTC orders remain active until canceled, providing more flexibility for long-term traders.
- Automation: You don’t need to constantly monitor the market, as the order will execute when the conditions are met.
What Is an Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Order and When Should You Use It?
An Immediate or Cancel (IOC) order is a type of Forex order that is designed to be filled immediately, either in full or partially. If any portion of the order cannot be filled instantly, the remaining part is automatically canceled. IOC orders are particularly useful for traders who want to execute trades quickly, but not at the expense of leaving parts of the order open.
1. How IOC Orders Work
When an IOC order is placed, it’s executed at the best available price in the market. Any part of the order that is not filled immediately is canceled, meaning that the trader only ends up with the portion that was executed instantly.
- Partial Fills: IOC orders can be partially filled, with the unfilled portion being canceled immediately.
- Fast Execution: This type of order is often used by traders who prioritize speed and want to avoid having unfilled types of orders left on the market.
2. When to Use IOC Orders
- Volatile Markets: IOC orders are useful in volatile markets where prices change quickly, and traders need to act fast to capture opportunities.
- Avoiding Market Exposure: Traders who don’t want to leave pending orders in the market and risk slippage or large price gaps use IOC types of orders to limit exposure.
Advantages of IOC Orders:
- Speed: IOC orders ensure that any part of the order that can be filled immediately is executed, providing fast market access.
- Limit Exposure: By canceling the unfilled portion, traders reduce their risk of unintended price movements affecting their trades.
How to Combine Different Order Types for Risk Management in Forex?
Combining different order types in Forex is a smart way to enhance your risk management strategy. By using a combination of market, limit, stop-loss, and take-profit orders, traders can create a well-rounded plan that protects their capital while maximizing profit potential.
1. Combining Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
One of the most effective strategies for managing risk is to use both stop-loss and take-profit orders. These types of orders work together to automatically exit your position when the market reaches predefined levels.
- Example: If you open a long position, you can set a stop-loss below your entry price to minimize potential losses and a take-profit order above the entry price to secure profits if the market moves in your favor.
- Benefit: This strategy allows you to automate your exits, ensuring that your trades align with your risk-reward ratio without constant monitoring.
2. Using Trailing Stops with Limit Orders
A trailing stop can be combined with a limit order to protect profits while allowing for more upside potential. This is particularly useful in trending markets, where you want to give the trade room to grow while safeguarding against a sudden reversal.
- Example: After placing a limit order to buy a currency pair at a certain price, you can set a trailing stop to follow the market as it moves in your favor, automatically adjusting to lock in profits.
3. Hedge Strategies Using Different Orders
More advanced traders can combine different order types to hedge their positions. For example, you could use a sell stop order on a long position as a hedge against potential losses if the market moves against you.
- Benefit: Hedging allows you to limit downside risk without closing your main position, providing flexibility in managing volatile market conditions.
What Are the Key Differences Between Market and Limit Orders?
Both market orders and limit orders are commonly used in Forex trading, but they serve different purposes. Understanding their key differences helps traders choose the right order type depending on their goals, trading style, and market conditions.
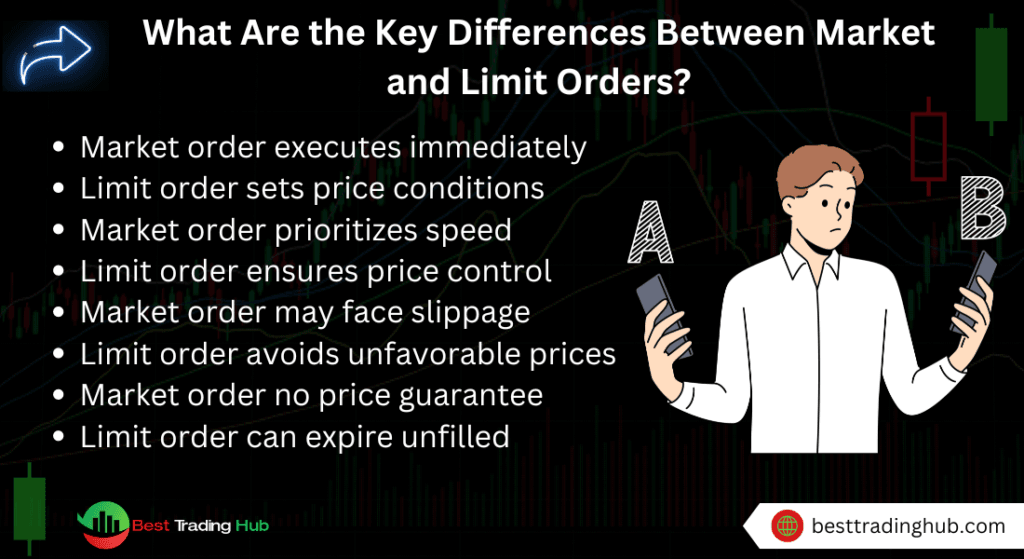
1. Market Orders: Instant Execution
A market order is executed immediately at the current market price. This order type is used when traders prioritize speed and want to enter or exit a position quickly.
- Advantages: Ensures quick execution, especially in fast-moving markets. Ideal for traders who need immediate entry or exit.
- Disadvantages: You may experience slippage, where the executed price differs from the expected price, especially during periods of high volatility.
2. Limit Orders: Price Precision
A limit order is executed only when the market reaches a specified price, giving traders more control over the price they pay or receive for a currency pair.
- Advantages: No slippage—traders know the exact price at which their trade will be executed. Useful for setting precise entry and exit points.
- Disadvantages: There’s no guarantee that the trade will be executed, especially in volatile markets where the price might not hit the desired level.
Key Differences:
- Execution: Market orders are executed immediately, while limit types of orders wait for the price to reach the specified level.
- Control: Limit orders provide more control over the price but come with the risk of non-execution, whereas market orders ensure execution but may result in unfavorable pricing.
When Should You Use One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO) Orders in Forex?
A One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO) order is a combination of two orders where, if one order is executed, the other is automatically canceled. This is a popular risk management tool used by traders who want to place two different types of orders and only keep one active.
1. How OCO Orders Work
OCO orders involve two conditional trades: one limit order and one stop order. If one of the trades is executed, the other order is automatically canceled. For example, you might place an OCO order to buy if the price breaks above resistance or sell if it breaks below support.
- Breakout Trading: OCO orders are particularly useful in breakout strategies, where traders anticipate a significant price movement but are unsure of the direction.
- Automation: Once the first order is executed, the second order is automatically canceled, removing the need for manual intervention.
2. When to Use OCO Orders
- Uncertain Market Direction: OCO orders are ideal when you expect the market to move significantly but are unsure whether it will break upward or downward. By placing two orders, you ensure you capture the movement regardless of the direction.
- Risk Management: OCO orders can help manage risk by ensuring that if one side of the trade is triggered, the opposite side is automatically canceled to avoid overexposure.
Advantages of OCO Orders:
- Flexibility: OCO types of orders allow traders to plan for multiple scenarios, ensuring that they don’t miss out on trading opportunities.
- Efficient Risk Management: Automatically canceling the second order reduces the need for manual adjustments and minimizes the risk of holding multiple positions.
What Are the Benefits of Using Time-Based Orders in Forex Trading?
Time-based orders allow traders to set specific time limits for their orders to remain active. These types of orders provide flexibility and control, ensuring that trades are executed or canceled based on a predetermined time frame, which can be beneficial for different trading strategies.
1. Day Orders
A day order is one of the most common time-based orders. It is valid for the duration of the trading day and will automatically expire at the end of the session if not executed.
- Short-Term Trading: Day types of orders are ideal for intraday traders who want to enter and exit positions within the same trading day without carrying positions overnight.
- Risk Management: By ensuring the order expires at the end of the day, traders can avoid the risk of market fluctuations during off-hours.
2. Good ‘Til Time (GTT) Orders
A Good ‘Til Time (GTT) order allows traders to specify an exact time and date for the order to remain active. If the order is not executed by that time, it will automatically be canceled.
- Flexibility: GTT types of orders offer more flexibility than day orders, allowing traders to control how long their orders remain active, particularly useful for swing traders who may hold positions for several days.
- Reduce Monitoring: With a GTT order, traders don’t need to constantly monitor the market, as the order will expire at the set time, providing peace of mind.
Advantages of Time-Based Orders:
- Customizable: Time-based orders provide flexibility, allowing traders to tailor their orders based on their specific trading style and time horizon.
- Efficient Risk Management: These types of orders help manage risk by ensuring that trades are executed or canceled within a certain time frame, avoiding unwanted market exposure.
How Can Bracket Orders Be Used for Protecting Profits and Limiting Losses?
A bracket order is a type of conditional order that involves placing three types of orders at once: a market or limit order, a stop-loss order, and a take-profit order. Bracket orders are primarily used for risk management, allowing traders to define both their maximum loss and desired profit level when opening a trade.
1. How Bracket Orders Work
When placing a bracket order, the trader opens a position (either a market or limit order) and simultaneously sets up a stop-loss order to protect against losses and a take-profit order to lock in profits. These two types of orders “bracket” the trade, ensuring it is closed once one of the two conditions is met.
- Stop-Loss Protection: The stop-loss part of the bracket order limits potential losses by automatically closing the trade if the market moves against the trader.
- Take-Profit Goal: The take-profit order ensures that the trade closes automatically when the desired profit level is reached, protecting gains.
2. When to Use Bracket Orders
- Defined Risk and Reward: Bracket orders are ideal for traders who want to define both the risk and reward parameters for their trades upfront. This approach removes emotional decision-making during volatile market conditions.
- Automated Trading: Bracket orders allow traders to set their entry, exit, and risk management levels in advance, reducing the need for constant market monitoring.
Advantages of Bracket Orders:
- Risk and Reward Defined: Traders know their maximum loss and profit potential before entering a trade.
- Hands-Off Trading: Once the trade is set up, there is no need for manual intervention, making it suitable for traders who prefer an automated approach.
What Tools and Platforms Are Best for Managing Forex Orders?
The success of any trading strategy often depends on using the right tools and platforms to manage your orders efficiently. Various trading platforms offer advanced features to help traders execute and manage Forex orders with precision.

1. MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5)
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5) are among the most popular trading platforms in Forex. They provide robust order management features, including the ability to place market, limit, stop-loss, and bracket types of orders.
- Advanced Charting: MT4 and MT5 offer comprehensive charting tools, allowing traders to analyze price action and make informed decisions.
- Expert Advisors (EAs): Both platforms support automated trading through Expert Advisors, enabling traders to execute and manage these types of orders without manual intervention.
2. cTrader
cTrader is another platform that offers high-level functionality for managing Forex types of orders. Known for its clean interface and advanced order execution options, it’s a favorite among professional traders.
- Depth of Market (DOM): cTrader offers a Depth of Market feature, allowing traders to see market liquidity levels and make better decisions on order placement.
- One-Click Trading: With one-click trading, traders can quickly execute these types of orders without delays, ensuring fast execution during volatile market conditions.
Key Features to Look For in Trading Platforms:
- Fast Execution: Choose a platform with fast execution to avoid slippage, especially in fast-moving markets.
- Customizable Orders: The ability to set and adjust various types of orders, including trailing stops and bracket types of orders, is crucial for active traders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the types of orders in Forex is crucial for traders who want to manage risk effectively and maximize their profit potential. Whether you’re using market, limit, stop-loss, or bracket orders, each order type plays a specific role in executing your strategy efficiently. By mastering these orders, you can ensure that your trades align with your goals and are protected against unexpected market movements.
Equally important to understanding Forex orders is choosing a Forex broker that offers the right tools and platform to manage these types of orders effectively. A good broker will provide fast execution, reliable customer support, and access to advanced order types such as stop-loss and trailing stop orders. Selecting the right broker can enhance your trading experience and help you implement the right order types more efficiently.












